AI/모두를 위한 ML (SungKim)
[ML alb 07-2] Meet MNIST Dataset
ferozsun
2021. 2. 20. 19:29
import tensorflow as tf
learning_rate = 0.001
batch_size = 100
training_epochs = 15
nb_classes = 10
# download mnist dataset
mnist = tf.keras.datasets.mnist
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data()
# normalizing data
x_train, x_test = x_train / 255.0, x_test / 255.0
# change data shape
print(x_train.shape) # (60000, 28, 28)
x_train = x_train.reshape(x_train.shape[0], x_train.shape[1] * x_train.shape[2])
x_test = x_test.reshape(x_test.shape[0], x_test.shape[1] * x_test.shape[2])
# change result to one-hot encoding
# in tf1, one_hot= True in read_data_sets("MNIST_data/", one_hot=True)
# took care of it, but here we need to manually convert them
y_train = tf.keras.utils.to_categorical(y_train, 10)
y_test = tf.keras.utils.to_categorical(y_test, 10)
# # Consider an array of 5 labels out of a set of 3 classes {0, 1, 2}:
# array([0, 2, 1, 2, 0])
# `to_categorical` converts this into a matrix with as many columns as there are classes. The number of rows
# stays the same. to_categorical(labels)
# array([[ 1., 0., 0.],
# [ 0., 0., 1.],
# [ 0., 1., 0.],
# [ 0., 0., 1.],
# [ 1., 0., 0.]], dtype=float32)
tf.model = tf.keras.Sequential()
tf.model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(units=10, input_dim=784, activation='softmax'))
tf.model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer=tf.optimizers.Adam(0.001), metrics=['accuracy'])
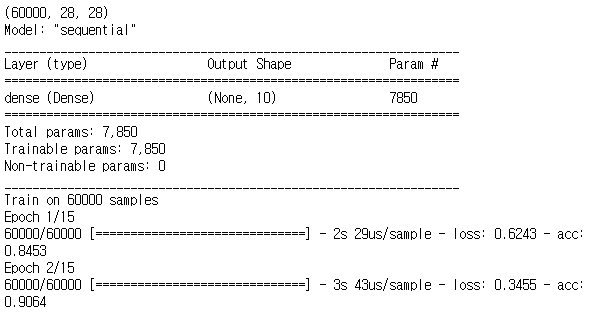
tf.model.summary()
history = tf.model.fit(x_train, y_train, batch_size=batch_size, epochs=training_epochs)
predictions = tf.model.predict(x_test)
print('Prediction: \n', predictions)
x_train
score = tf.model.evaluate(x_train, y_train)
print('Accuracy: ', score[1])[출력]
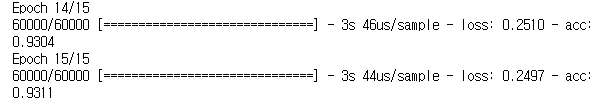

[Training epoch/batch]
neural network terminology에서:
▷ one epoch = one forward pass and one backward pass of all the training examples
▷ batch size = the number of training examples in one forward/backward pass.
The higher the batch size, the more memory space you'll need
▷ number of iterations = number of passes, each pas using [batch size] number of examples.
To be clear, one pass = one forward pass + one backward pass
Example: if you have 1000 training examples, and your batch size is 500, then it will take 2 iterations to complete 1 epoch.